tech layoffs
The technology industry, long regarded as one of the most dynamic and fast-growing sectors in the global economy, has recently been hit by a significant wave of layoffs.
As the world emerges from the pandemic and contends with economic uncertainties, many tech companies—ranging from startups to established giants—have initiated job cuts,
leaving thousands of employees suddenly jobless. These layoffs have sparked widespread discussion about the state of the tech industry, its growth prospects, and the factors driving this unexpected downturn.
The Scale of the Layoffs
Over the past two years, tech layoffs have reached alarming levels, with companies across various segments—software, hardware, e-commerce,
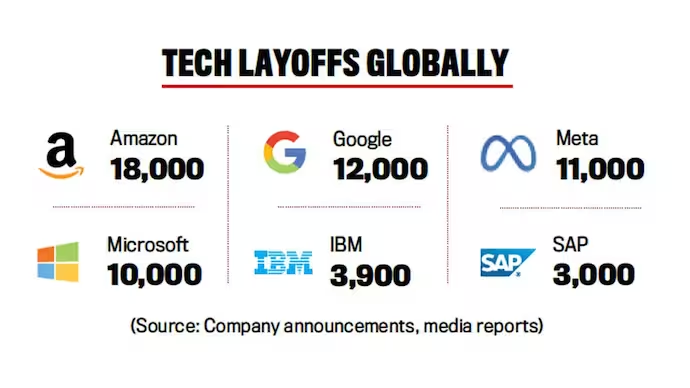
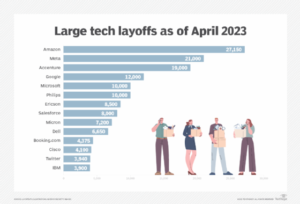
social media, and more—announcing mass reductions in their workforce. In 2023 alone, over 150,000 tech workers were let go, a stark contrast to the hiring frenzy that characterized the industry during the pandemic.
Many high-profile companies such as Meta (formerly Facebook), Amazon, Google, Microsoft, Twitter, and others have been forced to reduce their headcounts. Even some of the most promising startups that were flush with venture capital funding have been cutting costs by slashing jobs.
These layoffs have not been limited to specific roles or departments. Engineers, data scientists, marketing teams, HR, and even executives have found themselves on the receiving end of pink slips.

Factors Behind the Layoffs
Several key factors are contributing to this surge in tech layoffs, many of which are intertwined with broader economic conditions and shifts in the technology landscape.
- Post-Pandemic Market Correction: During the COVID-19 pandemic, the demand for digital products and services surged as remote work, online shopping, and virtual communication became essential.
- Tech companies responded by hiring aggressively to meet this increased demand. However, as the world returns to some semblance of normalcy, the demand for certain services has leveled off, leading companies to reassess their staffing needs.
- Overhiring During the Pandemic: Many tech firms overestimated the long-term demand for their services during the pandemic. Companies that doubled or tripled their workforce are now realizing
- that their growth projections were overly optimistic. With user engagement and revenues declining post-pandemic, these companies are cutting excess workforce to realign their operational scale with current realities.
- Macroeconomic Challenges: Global inflation, rising interest rates, and geopolitical tensions—particularly the war in Ukraine—have created a challenging economic environment. Investors are more cautious, and the availability of capital has decreased. As a result, tech companies,
- which are often heavily dependent on venture capital funding and stock market performance, have had to reduce expenses to maintain profitability. Reducing staff has been one of the primary cost-cutting measures.
- Shift in Consumer Behavior: Consumer preferences have also shifted. While certain sectors of technology, such as cloud computing and cybersecurity, continue to thrive, others, like consumer tech and social media,
- are seeing lower growth rates. The shift in demand patterns has left companies scrambling to adjust, with some product lines and services being scaled back or discontinued altogether.
- Regulatory Pressure: Increasing scrutiny from regulators, particularly in the U.S. and Europe, has added additional pressure on tech companies. Antitrust lawsuits, data privacy concerns,
- and calls for greater accountability have not only led to legal expenses but also created uncertainties around future business models. Companies facing regulatory hurdles are trimming their workforce to focus on core areas of compliance and innovation.
- Automation and Efficiency Initiatives: Ironically, technology itself has contributed to some of the layoffs. Automation, artificial intelligence, and machine learning tools have allowed companies to accomplish more with fewer human resources. Tasks that previously required
- large teams of employees can now be done with streamlined, AI-driven processes. This shift has led some tech companies to reduce their labor force, even as they continue to invest in advanced technologies.
Impact on Workers and the Industry
The consequences of tech layoffs extend beyond the employees who lose their jobs. These layoffs affect not only the livelihoods of workers but also the industry’s reputation as a beacon of innovation and opportunity.
For years, tech jobs were seen as highly stable, well-paying, and intellectually rewarding careers, drawing top talent from around the world. The recent wave of job cuts has shaken this perception and left many questioning the long-term security of their positions in the tech sector.
- Employee Morale and Productivity: Layoffs can have a profound effect on the morale of remaining employees. Those who survive the cuts often experience feelings of uncertainty and anxiety about the stability of their own jobs. Productivity can suffer as a result,
- as employees may become more focused on job security than innovation or performance. Furthermore, teams that are reduced in size often struggle to manage the same workload, leading to burnout and decreased efficiency.
- Loss of Innovation: Another downside of layoffs is the potential stifling of innovation. Tech companies thrive on creativity and problem-solving, but widespread job cuts can disrupt this dynamic.
- When experienced employees leave, they take their institutional knowledge with them, and teams may lose valuable perspectives that could have led to breakthroughs. In many cases,
- companies that aggressively reduce headcount struggle to maintain the same pace of innovation, which can lead to diminished competitive advantages over time.
- Diversity and Inclusion Setbacks: Tech layoffs could also set back progress in diversity and inclusion efforts. In recent years, many tech companies have committed to improving the representation of women, minorities,
- and other underrepresented groups in their workforces. However, during layoffs, these gains can be jeopardized, as the burden of cuts may disproportionately affect more vulnerable populations.
Long-Term Outlook for the Tech Industry
Despite the current turbulence, most experts agree that the long-term outlook for the technology industry remains positive. Technology continues to
be a major driver of economic growth, and areas such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, biotech, and green technology hold significant promise for the future.
While layoffs may be painful in the short term, they are also part of the cyclical nature of business, where periods of contraction are often followed by renewed growth.
The key for tech companies moving forward will be learning to adapt to new realities. For some, this may mean shifting their focus to emerging technologies,
while others may need to rethink their business models or diversify their revenue streams. For workers affected by the layoffs, reskilling and upskilling in areas of high demand will be crucial to remaining competitive in the job market.
Conclusion
The wave of tech layoffs that has swept through the industry in recent months is a sobering reminder that even the most prosperous sectors are not immune to economic downturns and shifting market dynamics.
While the layoffs are undoubtedly challenging for the individuals affected and the industry as a whole, they also present an opportunity for reflection, adaptation, and eventual renewal.
Tech companies will need to navigate these turbulent times with care, ensuring that their workforce strategies are aligned with both current challenges and future opportunities.